
To copy the file boot.img from the remote computer Host1, type: tftp -i Host1 get boot. Because the tftp protocol doesn't support user authentication, the user must be logged onto the remote computer, and the files must be writable on the remote computer. Transfers the file source on the local computer to the file destination on the remote computer. Transfers the file destination on the remote computer to the file source on the local computer. If a file transfer is successful, the data transfer rate is displayed. Use this mode when transferring text files. This mode converts the end-of-line (EOL) characters to an appropriate format for the specified computer. If you don't use the -i option, the file is transferred in ASCII mode. Use this mode when transferring binary files. In binary image mode, the file is transferred in one-byte units. Specifies binary image transfer mode (also called octet mode). A tftp server service is no longer provided by Microsoft for security reasons. Installing the tftp client is not recommended for systems connected to the Internet. The tftp protocol doesn't support any authentication or encryption mechanism, and as such can introduce a security risk when present. tftp is typically used by embedded devices or systems that retrieve firmware, configuration information, or a system image during the boot process from a tftp server. Transfers files to and from a remote computer, typically a computer running UNIX, that is running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (tftp) service or daemon.

#3d demon tftp client windows
Source base, with added patches by Markus Gutschke and Gero Kulhman.Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 There is also a SNTP receiver in the package to coordinate with the Simple Network Time Protocol. The utility also includes a TFTP client, a DNS server, a DHCP server, and a Syslog server.
#3d demon tftp client free
It was derived from, but has substantially diverged from, an OpenBSD Tftpd64 is a free TFTP server for Windows. These access restrictions are likely to be site- and server-specific. Therefore, the remote server will probably implement some kinds of access The TFTP protocol provides no provisions for authentication or security. Toggle packet tracing (a debugging feature.) Timeout total-transmission-timeout Set the total transmission timeout, in seconds. Rexmt retransmission-timeout Set the per-packet retransmission timeout, in seconds. Enable literal mode to prevent special treatment of the ':' character (e.g. If the remote-directory form is used, the remote host is assumed to be a UNIX system or another Hostname specified becomes the default for future transfers. Has already been specified, or a string of the form host:filename to specify both a host and filename at the same time. The destination can be in one of two forms: a filename on the remote host, if the host remote-directory Put a file or set of files to the specified remote file or directory. Put file put localfile remotefile put file1 file2 file3. Mode transfer-mode Specify the mode for transfers transfer-mode may be one of ascii (or netascii) or binary (or octet.) The default is When set, this mode prevents special treatment of ':' in filenames.
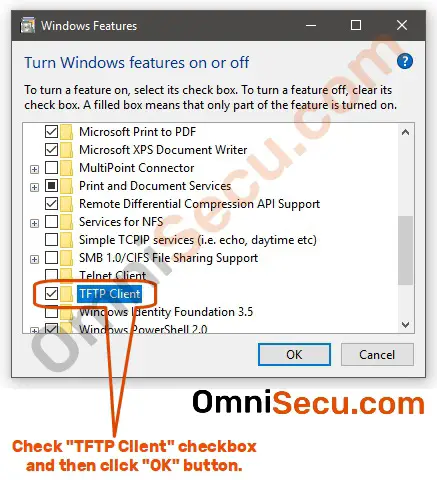
A remote filename can be in one of two forms: a plain filename on the remote host, if the host hasĪlready been specified, or a string of the form host:filename to specify both a host and filename at the same time. Get a file or set of files from the specified sources. Get file get remotefile localfile get file1 file2 file3. To use the connect command the remote host can be specified as part of the get or put commands.

Transfers thus, the connect command does not actually create a connection, but merely remembers what host is to be used for transfers. Note that the TFTP protocol, unlike the FTP protocol, does not maintain connections between Print help informationĬonnect host Set the host (and optionally port) for transfers. Once tftp is running, it issues the prompt tftp> and recognizes the following commands: Print the version number and configuration to standard output, then exit gracefully. R port:port Force the originating port number to be in the specified range of port numbers. m mode Set the default transfer mode to mode. Used to avoid special processing of ':' in a file name. Must be specified last on the command line.ĭefault to literal mode. c command Execute command as if it had been entered on the tftp prompt. Host for future transfers (see the connect command below.)Ĭonnect with IPv4 only, even if IPv6 support was compiled in. The remote host may be specified on the command line, in which case tftp uses host as the default Tftp is a client for the Trivial file Transfer Protocol, which can be used to transfer files to and from remote machines, including some very


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
